Operational forecasting and decision support system for São Francisco River
With a length of 2,914 kilometres, the São Francisco River is one of the longest rivers in South America. 11 reservoirs are located in the São Francisco River and its tributaries. The Três Marias hydropower reservoir is the largest one on the upper river. This dam was built during the 1950s, and the reservoir has a total capacity of 19.5×109m³, which gives the reservoir a strategic importance for the water and energy supply in Brazil. The dam serves multiple purposes: hydropower generation, flood control, navigation, municipal and industrial water supply and irrigation. In collaboration with the Brazilian Institute of Technology for Development (LACTEC), Deltares has developed a decision support system for reservoir management of the São Francisco River reservoir system.
Operational management of the São Francisco River reservoir system
The government controlled electric energy company CEMIG (Brazil) is responsible for the short-term management of the São Francisco River reservoir system. In general, the following reservoir management policies are applied:
- In order to maximize power production, turbine flow is preferred against spillway discharge.
- The maximum fore bay elevation is time dependent and limited by the reservoir’s maximum operating limit or a lower operational limit that ensures sufficient flood control storage during the wet season. This policy conflicts with the target of maximizing power production.
- High discharge thresholds are defined for certain locations in the reservoir system, and these high discharge thresholds should not be exceeded.
- Large outflow gradients are should be avoided.
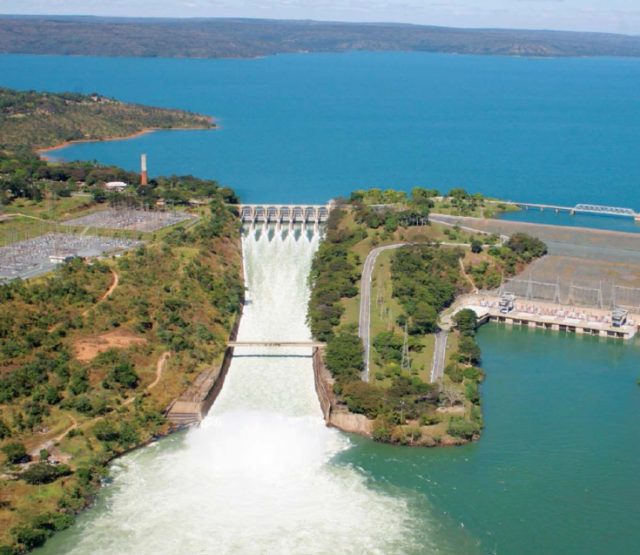

Decision support system
The interaction of reservoirs due to cascading effects and the conflicting management policies make the reservoir management a complex task. In collaboration with the Brazilian Institute of Technology for Development (LACTEC), Deltares has developed a decision support system for reservoir management of the São Francisco River reservoir system.
The operational forecasting and decision support system (DSS) is based on the open data handling platform Delft-FEWS and integrates different sources of ground information, remote sensing data and numerical weather predictions with hydrological and hydrodynamic models to generate short-term flow forecasts for up to 15 days ahead for each of the eleven reservoirs.
These forecasts are fed into the real-time control toolbox RTC-Tools. RTC-Tools determines an optimal release strategy for the forecast horizon with the help of deterministic and multi-stage stochastic optimization methods.
The reservoir management is formulated as an optimisation problem that incorporates a mathematical model of the reservoir system. The different management policies are objectives and constraints of the optimisation problem.
Read more in the paper “Short-Term Reservoir Optimization for Flood Mitigation under Meteorological and Hydrological Forecast Uncertainty”
