Floating solar panels
Floating solar panels are an increasingly common sight in the water-rich Netherlands as a way of producing sustainable energy. Small-scale experiments are being conducted with floating solar panels in various locations here, both on lakes and on the North Sea. The first large solar farms have been installed on water in countries such as Korea, China, Japan and America to achieve the enormous upscaling of renewable energy production. However, the effects on water quality and the aquatic ecology of these floating solar installations are still largely unknown. The impact on ecosystem services and our living environment are therefore unclear as well.
Deltares is studying the direct and indirect effects of solar farms on water. That knowledge is needed to make good decisions about the design and management of floating solar farms on a large scale. We are also looking at the various goals and functions of the water. This knowledge effort for solar energy involves working with, among others, water authorities, municipal and provincial authorities, the private sector and other research institutes.
Our ambition is to have a clearer understanding of the impact of floating solar panels in three years from now. We want to know:
- what the effects are
- whether the effects are positive or negative
- how big the effects are
- whether negative effects can be mitigated by making design adjustments
- whether it is possible to establish acceptable permit conditions from the point of view of water quality and the ecology
In this way, we will ensure that decisions can be taken on the basis of sound knowledge. For example, we can ensure that water authorities not turn down permit applications by being over-cautious because of a lack of knowledge. Our aim is also to make sure that we still have clean, healthy and sufficiently fresh surface water.
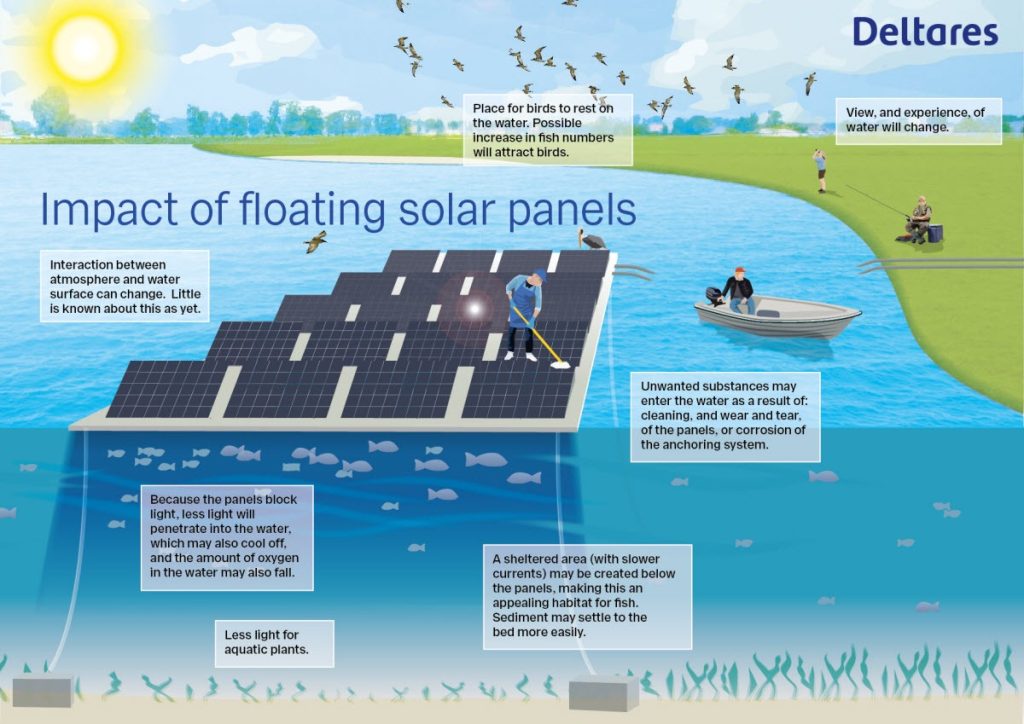
Impact of floating solar panels
The potential positive and negative effects of a floating solar farm are:
- Interaction between atmosphere and water surface can change. Little is known about this as yet
- Because the panels block light, less lights will pentrate into the water, which may also cool off, and the amount of oxygen in the water may also fall
- Less light for aquatic plants
- A sheltered area (with slower currents) may be created below ghe panels, making this an appealing habitat for fish. Sediment may settle to the bed more easily
- Unwanted substances may enter the water as a result of cleaning, and wear and tear, of the panels, or corrosion of the anchoring system
- View, and experience, of water will change
- Place for birds to rest on the water. Possible increase in fish numbers will attract birds
Multiple use of space
Innovative solutions that facilitate the multiple use of space, such as floating solar farms in combination with water storage or improvements to nature and water quality, are high on the global agenda. Ideas such as combining hydroelectric reservoirs with floating solar panels are put forward regularly. The idea of solar atolls on the IJsselmeer lake is another good example in this context.
But the combination of floating solar farms with new developments such as marine farms is also being considered. To establish a picture of feasibility and the effects on the water system, Deltares uses existing hydrodynamic and ecological models to simulate and predict the situation. We can deploy these models to describe the effects, such as the reduction of light penetration or possible changes in the flora and fauna.
We are also looking at the interaction between solar panels and waves. Do these floating structures dampen waves and can they cope with the wave climate on the North Sea, for example? Which configuration of solar panels results in the maximum dampening effect? We can answer these questions using our physical wave facilities and wave models. This knowledge is essential to establish win-win situations and facilitate the multiple use of space.
Available knowledge about floating solar panels
Although many questions still have to be answered, Deltares has already conducted a range of studies on floating solar panels and energy. They include:
- A reconnaissance study looking at solar atolls to upgrade nature and create space for sustainable energy production. Publication: Solar atolls result in space for nature and sustainable energy (in Dutch).
- Deltares has collaborated with STOWA (Foundation for applied water research of the regional Dutch waterboards) and Rijkswaterstaat on a guide to permit procedures for floating solar farms (in Dutch).
- International literature study of the effects of floating solar systems on water quality and ecology (2020, Dionisio Pires and Loos).
- Monitoring Recommendations: The aim of the monitoring recommendations (MeetAdvies) is to acquire data about these possible effects. The aim is to store as much of the collected data centrally and openly as far as is possible so that they are available for analysis.
- Pilot Offshore seaweed and floating energy in the Netherlands, part of European Union Horizon 2020 project UNITED (Multi-Use offshore platforms demoNstrators for boostIng cost-effecTive and Eco-friendly proDuction in sustainable marine activities).
- Modelling projects e.g. effects of the Floating solar photovoltaic systems on water temperature and mixing of the reservoir in Andijk.
Related projects
Related content
-
Hydropower
-
Offshore wind energy
-
Heating and cooling networks for a carbon-free built environment
-
Aquathermal energy: heating and cooling with water
-
Aquifer thermal energy storage
-
Tidal energy and energy from temperature difference and blue energy
-
Wave energy: supplementing the energy transition
-
Energy transition: responsible choices and sustainable use

